How to Treat Heartworm Disease in Dogs
Heartworm disease is a potentially deadly parasitic infection in dogs. Without treatment, a dog with heartworm disease will eventually die. Although t
Spaying dogs is a common practice, but what is it, how is it done, and how does it affect your dog? Learn why you might want to have your dog spayed so you can decide whether or not to go forward with the procedure. Many people confuse spaying with neutering. Spaying is a surgical procedure to remove the ovaries and uterus from female dogs and neutering is a surgical procedure to remove the testicles from male dogs.
The word "spay" is a common term for ovariohysterectomy. This is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of a female dog's reproductive organs. A spay must be performed under general anesthesia by a veterinarian. The procedure will permanently stop the dog from having heat cycles and being able to reproduce. In some cases, veterinarians will remove just the ovaries and leave the uterus intact. This procedure is called an ovariectomy, but its effects are essentially the same as with an ovariohysterectomy.
Dogs are typically spayed in order to eliminate the possibility of reproduction, but there are many other benefits to the procedure, including:
Dogs are often spayed around the age of six months, before the reproductive system is active. Puppies adopted from animal shelters may be spayed even earlier to ensure that the procedure is performed. In some cases, it is beneficial to delay spaying, for instance when a dog has a recessed vulva that predisposes it to infections or to reduce the risk of orthopedic diseases in some large breeds.
While spaying is best thought of as a preventative measure performed in young animals, older dogs may need to be spayed after their show or reproductive career is over or to treat diseases of the ovaries and uterus and other medical conditions.
Complications are uncommon during a routine spay. However, the procedure is not without risks. As with any surgical procedure, potential complications include anesthesia reaction, excessive bleeding, bruising, and infection. Some dogs may develop hormone-related urinary incontinence.
It's important for a veterinarian to thoroughly examine the dog and perform lab work prior to surgery. These procedures may reveal health issues that increase the dog's risk of complications during and after surgery. In cases where an underlying health problem is found, the veterinarian may recommend further diagnostics, like additional lab work, radiographs, ultrasound, and additional lab tests prior to anesthesia. The vet may adjust the anesthesia protocol for the dog's safety. Or, the vet may decide that anesthesia is not safe for the dog at this time.
Overall, the prognosis for recovery is excellent in healthy dogs.
Spaying is routine surgery. In general, the full process around the spay will last about one to two hours (from the time anesthesia starts until the dog is awake). The spay surgery itself typically takes about 30 minutes. Here's what happens during the different phases of the spaying surgery:
Most dogs recover very quickly from spay surgery. However, it is important to keep your pup rested and relatively inactive for a week or two after the surgery to allow for proper healing. Running and jumping too soon can irritate the tissue in the abdomen, causing inflammation and pain. It can also make sutures tear, possibly causing internal bleeding or the incision to open up. Too much activity can slow the healing process and lead to complications.
The dog must also be kept from licking the incision. As the incision heals, discomfort or itching may lead the dog to lick the area. This introduces bacteria and causes irritation, which can lead to an infection. In extreme cases, dogs can also chew out their sutures.
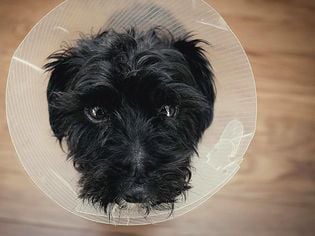
The vet may send the dog home with an Elizabethan collar, known informally as an "e-collar." The collar resembles a lampshade and blocks the dog from licking the incision. Most dogs dislike the collar, but it's better than having to go back to surgery or risk infection of the surgical wound.

Heartworm disease is a potentially deadly parasitic infection in dogs. Without treatment, a dog with heartworm disease will eventually die. Although t

With a close to 100 percent mortality rate once symptoms appear, rabies is one of the most devastating viruses on the planet. It can infect any mammal

The Thai Ridgeback is a muscular medium to large dog breed with primitive roots in Thailand. This athletic breed is known for the ridge of hair along
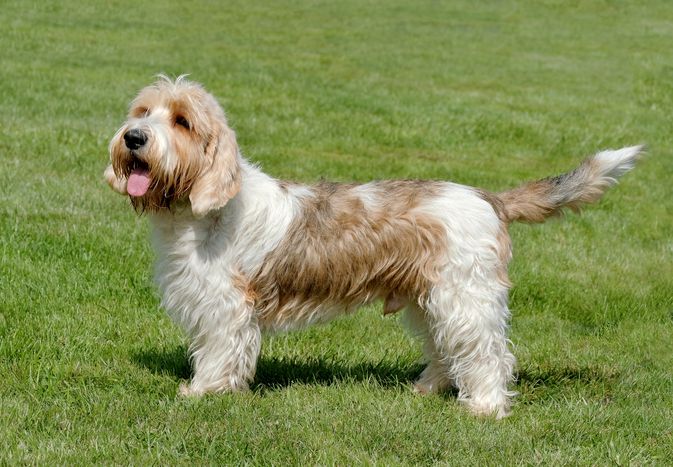

The Petit Basset Griffon Vendéen, "PBGV" or "Petit" for short, is a small, shaggy-coated scent hound developed in France. Known for th

Many dogs are classified as herding dog breeds—sheepdogs, cattle dogs, shepherds, or collies. Herding dogs come in all shapes and sizes from all over

The Mudi is a medium-sized herding breed from Hungary with a wavy coat, pointed ears, and coat colors that can include a unique merle pattern. As a wo

The Norwich Terrier is an affectionate and curious dog named for its hometown in England. Standing at just 10 inches tall, the small-but-mighty Norwic

Toy poodles, along with standard poodles and miniature poodles, are famously known for their proven excellence in dog shows. Their curly and voluminou
We are a comprehensive and trusted information platform dedicated to delivering high-quality content across a wide range of topics, including society, technology, business, health, culture, and entertainment.
From breaking news to in-depth reports, we adhere to the principles of accuracy and diverse perspectives, helping readers find clarity and reliability in today’s fast-paced information landscape.
Our goal is to be a dependable source of knowledge for every reader—making information not only accessible but truly trustworthy. Looking ahead, we will continue to enhance our content and services, connecting the world and delivering value.